Drone sightings around the world are rapidly increasing, presenting a complex interplay of technological advancement, regulatory challenges, and societal impact. This global phenomenon necessitates a comprehensive understanding of the various drone types, their applications, and the consequences of their proliferation. This analysis explores the geographic distribution of sightings, the diverse purposes of drones, and the multifaceted responses from various sectors and governments.
The rise in drone usage, driven by technological innovation and decreasing costs, has led to a corresponding increase in reports of unauthorized drone flights. These sightings pose significant challenges to aviation safety, national security, and public perception of privacy. Understanding the underlying factors driving this increase, along with the effectiveness of current regulatory frameworks and detection technologies, is crucial for mitigating future risks.
Types of Drones and Their Purposes: Drone Sightings Around The World
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), commonly known as drones, have proliferated globally, leading to a diverse range of applications across various sectors. Understanding the different types of drones and their associated purposes is crucial for assessing their impact on society and addressing potential challenges. This section details the key classifications of drones and their prevalent uses, highlighting technological advancements driving their evolution.
Increased global drone sightings necessitate improved counter-drone technologies. Understanding the complexities of drone detection and mitigation is crucial, as highlighted by the challenges faced in filming, as seen in the fights camera action context. This understanding informs the development of effective strategies for managing the risks associated with unauthorized drone activity worldwide.
Consumer Drones
Consumer drones are primarily designed for recreational and personal use. These drones are typically smaller, lighter, and more affordable than their commercial or military counterparts. They are often equipped with high-resolution cameras and user-friendly interfaces, making them accessible to a wide range of users.
- Purpose: Aerial photography and videography, recreational flying, and basic surveillance.
- Technological Advancements: Improved camera stabilization, longer flight times, obstacle avoidance systems, and enhanced ease of use through simplified control interfaces and apps.
Commercial Drones
Commercial drones represent a significant segment of the drone market, employed across a wide spectrum of industries. These drones are often larger and more robust than consumer drones, capable of carrying heavier payloads and operating for extended durations. Their applications are driven by the need for efficient and cost-effective solutions in various sectors.
- Purpose: Infrastructure inspection (bridges, power lines), precision agriculture (crop monitoring, spraying), delivery services (package delivery, medical supplies), search and rescue operations, surveying and mapping, filmmaking, and real estate photography.
- Technological Advancements: Increased payload capacity, extended flight range, advanced sensor integration (thermal, multispectral), improved data processing and analysis capabilities, and enhanced autonomy through sophisticated flight control systems.
Military Drones
Military drones, also known as unmanned combat aerial vehicles (UCAVs), are designed for military operations, encompassing a wide range of capabilities. These drones are often equipped with advanced sensors, weaponry, and communication systems, enabling them to perform complex tasks in challenging environments. Their development and deployment are subject to stringent regulations and ethical considerations.
- Purpose: Surveillance and reconnaissance, target acquisition, precision strikes, combat support, and intelligence gathering. Examples include the MQ-9 Reaper and the General Atomics Avenger.
- Technological Advancements: Enhanced stealth capabilities, improved sensor resolution and range, increased payload capacity for weapons and sensors, autonomous flight capabilities, and advanced communication systems for real-time data transmission.
Impact of Drone Sightings on Different Sectors

The proliferation of drones has led to a significant increase in drone sightings globally, impacting various sectors in diverse ways. These impacts range from disruptions to air travel and national security concerns to shifts in public perception regarding privacy and safety. Understanding these impacts is crucial for developing effective regulatory frameworks and mitigating potential risks.
Aviation Industry Disruptions
Drone sightings near airports and other airspace have caused significant disruptions to the aviation industry. Incidents involving drones near runways have resulted in airport closures, flight delays, and diversions, leading to substantial economic losses for airlines and airports. For example, the Gatwick Airport drone incident in 2018 caused significant delays and cancellations, affecting thousands of passengers and costing millions of pounds.
The uncertainty surrounding the origin and intent of these drones often necessitates precautionary measures, prioritizing safety over operational efficiency. These disruptions highlight the vulnerability of air travel to unauthorized drone activity.
Increased drone sightings worldwide raise concerns regarding airspace safety and potential misuse. The scale of these observations varies, with some reports detailing the presence of unusually large unmanned aerial vehicles, such as those described on this website detailing a giant drone and its capabilities. Further research is needed to fully understand the implications of these increasingly frequent and diverse drone appearances globally.
Law Enforcement and National Security Implications
Drone sightings pose challenges to law enforcement and national security. Drones can be used for illicit activities, including smuggling contraband, conducting surveillance, or even carrying explosives. Their small size and maneuverability make them difficult to detect and intercept, requiring specialized counter-drone technologies and strategies. Law enforcement agencies face the challenge of identifying and apprehending drone operators, while national security agencies must address the potential for drones to be used in terrorist attacks or other malicious activities.
The increasing sophistication of drone technology further complicates these challenges.
Public Perception and Concerns
The rise in drone sightings has influenced public perception and raised concerns about privacy and safety. The potential for drones to be used for surveillance raises concerns about unauthorized monitoring of private property and individuals. Accidents involving drones, such as those resulting in injuries or property damage, contribute to public apprehension. This necessitates a public discourse regarding the responsible use of drones and the development of regulations that balance innovation with safety and privacy considerations.
Public trust in the ability of authorities to manage the risks associated with drone technology is also crucial.
International Responses to Drone Sightings
Different countries have adopted varied approaches to managing the increasing number of drone sightings. Some countries have implemented strict regulations regarding drone operation, including licensing requirements, geographical restrictions, and limitations on drone capabilities. Other countries have focused on developing counter-drone technologies and strategies to detect and neutralize unauthorized drones. The level of regulatory oversight and technological advancements in counter-drone measures vary considerably across nations, reflecting differences in national priorities and technological capabilities.
International collaboration is essential to establish consistent standards and best practices for managing the risks associated with drone operations globally.
Regulations and Responses to Drone Sightings
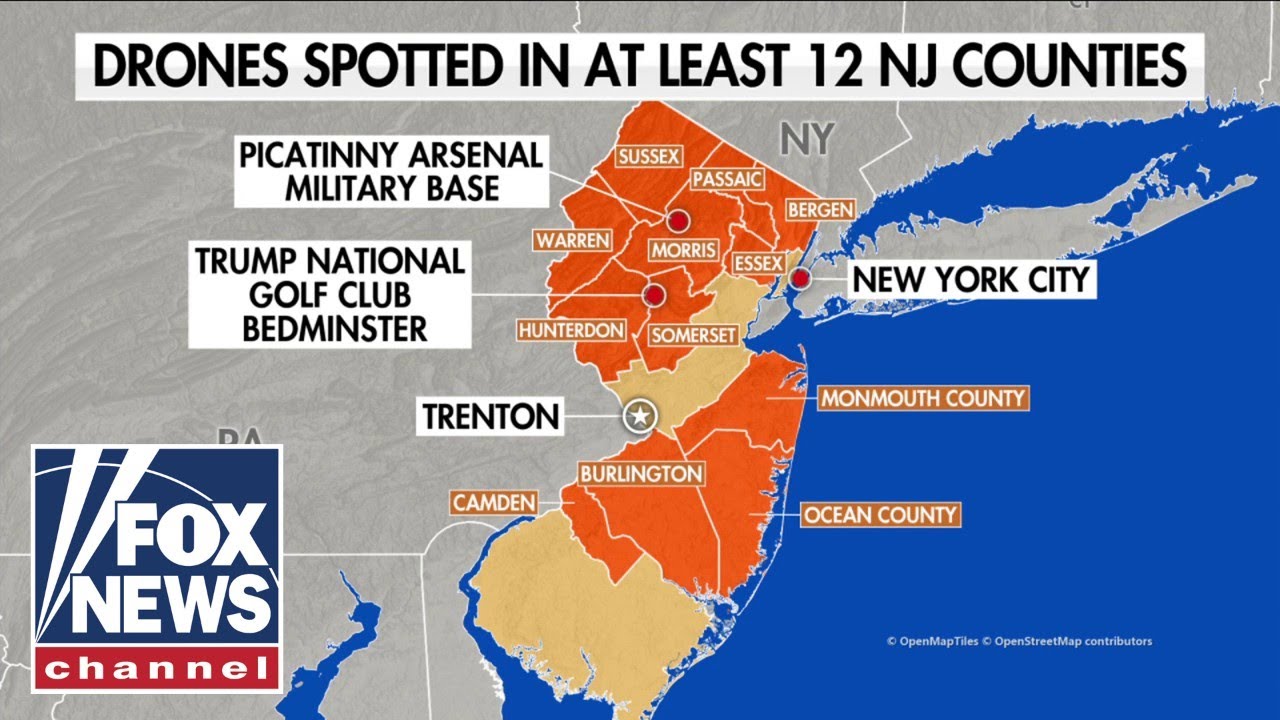
The proliferation of drones has necessitated the development of comprehensive regulatory frameworks and robust response mechanisms worldwide. These address concerns regarding airspace safety, privacy, security, and the potential misuse of this technology. The effectiveness of these regulations and responses varies significantly across jurisdictions, influenced by factors such as technological advancements, national security priorities, and societal acceptance.
Existing Drone Regulations and Laws, Drone sightings around the world
National and international regulations governing drone operation are diverse but generally address aspects like registration, licensing, operational limitations (altitude, distance from airports, etc.), and restrictions on payload and intended use. Many countries require drone operators to register their devices and obtain permits for commercial operations. These regulations often stipulate operational guidelines to prevent collisions with manned aircraft, protect privacy, and ensure public safety.
For instance, the United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) has established a comprehensive regulatory framework, including Part 107 for commercial operations, outlining specific requirements for drone pilots and flight operations. Similarly, the European Union’s framework for drones, known as the U-space initiative, aims to integrate drones safely into the existing airspace. These regulatory frameworks are continuously evolving to adapt to the rapidly changing drone technology landscape.
Drone Detection and Tracking Methods
Several methods exist for detecting and tracking drones, ranging from visual observation to sophisticated technological solutions. Visual detection relies on human observers, often aided by binoculars or cameras. However, this method is limited by range and visibility conditions. More advanced methods include radar systems, which can detect the drone’s radar signature, and radio frequency (RF) detection systems, which identify the drone’s control signals.
Acoustic sensors can detect the drone’s engine noise, and optical systems, such as cameras and infrared sensors, can visually identify drones, even at night or in low-light conditions. Advanced systems often integrate multiple detection methods for improved accuracy and reliability. These systems can be deployed in fixed locations, such as airports or critical infrastructure sites, or mounted on mobile platforms for wider coverage.
Mitigation Strategies for Unauthorized Drone Flights
Mitigation strategies for unauthorized drone flights involve a multi-layered approach. These include preventative measures, such as public awareness campaigns educating drone operators about regulations and safe operating practices. Technological solutions like drone detection and tracking systems play a crucial role in identifying unauthorized drones. Response strategies encompass actions taken once an unauthorized drone is detected. These can range from issuing warnings to deploying counter-drone technology to neutralize the threat.
Counter-drone technology includes various methods, such as jamming signals, deploying nets to physically capture drones, or using directed energy weapons to disable the drone. The selection of appropriate mitigation strategies depends on the specific risk assessment, considering factors such as the drone’s potential threat level, the location, and available resources.
Comparative Analysis of Drone Regulations
| Country | Registration Requirements | Licensing Requirements | Enforcement Mechanisms |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Required for most commercial operations; voluntary for recreational use. | Part 107 certification required for commercial operations. | FAA enforcement, including fines and legal action. |
| United Kingdom | Registration required for most drones weighing over 250g. | Operator competency required for commercial operations. | Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) enforcement, including fines and legal action. |
| Canada | Registration required for drones weighing over 250g. | Basic safety knowledge test required for commercial operations. | Transport Canada enforcement, including fines and legal action. |
Array
The global drone market is poised for significant expansion in the coming decade, driven by technological advancements, decreasing costs, and expanding applications across diverse sectors. This growth will inevitably lead to an increase in drone sightings, necessitating proactive adaptation in regulatory frameworks and safety protocols. Predicting the precise trajectory of this growth requires careful consideration of technological progress, societal acceptance, and regulatory responses.The anticipated advancements in drone technology will significantly influence the nature and frequency of drone sightings.
Improved battery technology, autonomous navigation systems, and enhanced sensor capabilities will enable longer flight times, more complex missions, and greater operational efficiency. These advancements will simultaneously increase the potential benefits of drone usage while also raising concerns about privacy, security, and airspace management.
Growth Projections and Sectoral Implications
Several market research firms predict a substantial increase in the global drone market size. For instance, a report by Grand View Research projects the market to reach a valuation exceeding $50 billion by 2030, fueled by increasing demand from sectors like agriculture, logistics, infrastructure inspection, and surveillance. This growth will translate to a higher frequency of drone sightings in urban and rural areas alike.
The agriculture sector, for example, is expected to witness a considerable rise in drone usage for precision farming, leading to more frequent sightings over agricultural lands. Similarly, the logistics industry’s adoption of drone delivery systems will increase the visibility of drones in urban airspace. The infrastructure inspection sector will also contribute to more sightings, as drones become increasingly used to monitor bridges, pipelines, and power lines.
Technological Advancements and Their Impact
Beyond longer flight times and enhanced autonomy, future drone technology will incorporate advanced features such as swarm intelligence, enabling coordinated operations of multiple drones for large-scale tasks. Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) will further improve drone navigation, obstacle avoidance, and data analysis capabilities. These advancements will enhance the efficiency and safety of drone operations, but also present new challenges in terms of managing complex airspace interactions and preventing potential malfunctions.
For instance, the increasing sophistication of AI-powered drones could lead to more unpredictable flight patterns or raise concerns about autonomous decision-making in critical situations.
Future Challenges in Drone Regulation and Safety
The rapid growth of the drone industry necessitates a robust and adaptable regulatory framework to address safety and security concerns. Challenges include ensuring effective airspace management to prevent collisions, establishing clear guidelines for data privacy and security, and developing mechanisms for identifying and tracking unauthorized drone operations. The increasing use of drones for commercial and public safety purposes requires clear protocols for certification, licensing, and operational procedures.
International cooperation will be crucial in establishing consistent standards and preventing conflicts in cross-border drone operations. Moreover, the development of counter-drone technologies will be necessary to mitigate risks associated with malicious use of drones.
Infographic: Future of Drone Technology
The infographic would feature a central image of a futuristic cityscape with various types of drones operating seamlessly within the airspace, including delivery drones, inspection drones, and autonomous aerial vehicles. This would visually represent the predicted integration of drones into everyday life. Three distinct sections would radiate from the central image.Section 1: “Growth and Applications” – This section would display a bar graph showing projected market growth for the drone industry over the next decade, categorized by sector (agriculture, logistics, infrastructure, etc.).
The bar graph’s height would visually demonstrate the exponential growth expected.Section 2: “Technological Advancements” – This section would feature icons representing key technological advancements, such as AI, swarm technology, enhanced sensors, and improved battery life. Each icon would be accompanied by a brief description highlighting its impact on drone operations and safety.Section 3: “Regulatory Challenges” – This section would present a network diagram illustrating the complex interplay of stakeholders involved in drone regulation (government agencies, drone manufacturers, operators, etc.).
The lines connecting the stakeholders would represent the challenges in coordinating regulations and ensuring safety. The overall design would be clean, modern, and easily understandable, conveying the complex yet promising future of drone technology.
The global proliferation of drones presents both opportunities and challenges. While technological advancements continue to expand drone capabilities and applications, effective regulation and international cooperation are paramount to ensure safe and responsible drone operation. Future research should focus on enhancing drone detection technologies, improving regulatory frameworks, and fostering public awareness to mitigate potential risks and harness the benefits of this transformative technology.
The ongoing evolution of drone technology necessitates a dynamic and adaptive approach to regulation and public education to address the complex issues arising from increased drone sightings worldwide.
Essential Questionnaire
What are the most common types of drones involved in sightings?
Consumer drones for recreational purposes are frequently sighted, along with commercial drones used for photography, videography, and delivery. Military drones are also occasionally reported, though often in more restricted areas.
How are drone sightings impacting insurance costs?
Increased drone sightings are leading some insurers to raise premiums for airports and other infrastructure potentially vulnerable to drone-related incidents, reflecting the increased risk assessment.
What countermeasures are being developed to address unauthorized drone flights?
Countermeasures range from radio frequency jamming and detection systems to specialized anti-drone weaponry and advanced radar technologies. Research into artificial intelligence for drone identification and autonomous response is also underway.
Are there international agreements regarding drone regulations?
While no single global agreement exists, various international organizations are working towards establishing standards and best practices for drone operation and safety, often focusing on airspace management and information sharing.
